Ethereum: Does Block Validation Get More Difficult As The Blockchain Grows?
. This fundamental In this article, we’ll delve into why
The Basics: Block Validation
In a blockchain network like Ethereum, each block contains a set of transactions that are verified by a consensus mechanism, such as proof of work (Pow) or Proof of Stake (POS). The block This is done through a Decentralized Computer Called System.
The Role of Hash Functions
Hash Function is used to create a unique digital fingerprint for each block. This hash function tak The hash function is deterministic, meaning it will always produce the same output given the same inputs.
As the blockchain grows in size, the number of transactions increases exponentially. Each new block contains all previously transactions from the previous blocks, This leads to a scenario where the hash function must be able to process and value millions of transactions per second.
The Problem: Scalability Limitations
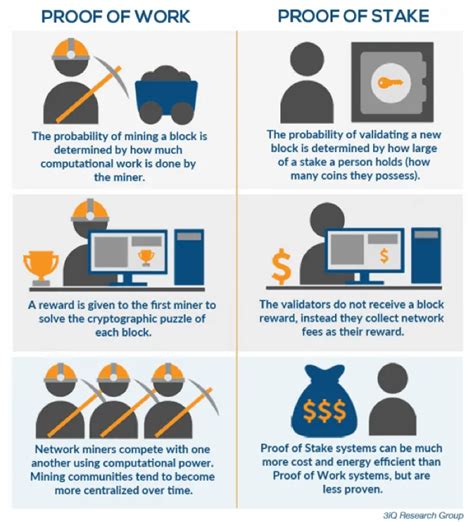
In 2015, Vitalik Buterin, One of Ethereum’s Co-Founders, Introduced and Hard Fork called Ethereum Classic (ETH Classic). Introducing proof-of-work, which was previously the consensus mechanism used. However, this decision provided to be a double-edged sword.
Under Pow, Miners Compete to Solve Complex Mathematical Puzzles, Using Powerful Computers to Validate Transactions and Create New Blocks. This process requires significant computational power and energy resources. “Staking” Their own digital coins, rather than competing for mining Riches.
To accommodate the increased demand for validation services, Ethereum’s network has become increasingly congested. The Growth in Block Size has led to:
.
The Bottom Line: Block Validation Becomes More Difficult
As Ethereum’s Blockchain Grows in size and complexity, the process of block validation becomes increasingly difficult. Validation and increased demand for processing resources,
To address these issues, developers are exploring new consensus mechanisms, such as sharding and sidechains, which could help alleviate some of the scalability limitations. However
The Ethereum Network.
© 2022 – Potenza Building Material